How Can We Help?
Installation serveur LAMP sur Ubuntu 18.04.03
Introduction
Cet article décrit l’installation de LAMP (Linux – Apache – MySQL – PHP) sur un serveur Ubuntu 18.04.03. En effet, par défaut , l’installation Ubuntu se fait sans Apache – MySQL – PHP
Installation LAMP
Installation Linux Ubuntu 18.04.03
Pour l’installation d’un serveur Ubuntu, voir article suivant : Installer serveur Ubuntu 18.04.03
Une fois votre serveur linux installé, connectez vous avec un compte sudo
Installation PHP
Pour choisir la version de PHP a installer il faut utiliser les dépôt gérer par ondrej
$ sudo
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ondrej/php
Une fois les dépôt installés, lancez l’installation de la version que vous souhaitez (7.0 , 7.1 , 7.2 , 7.3, …)
sudo apt install php7.1 php7.1-cli php7.1-common
sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-mysql
Installation de MySQL 8
L’installation de MySQL en version 8 se fait en trois étapes :
- ajout des dépôts de développement
- installation du serveur MySQL
- configuration des accès root au serveur MySQL
Dans cette première étape, Il faut mettre à jour les dépots MySQL pour votre serveur Ubuntu
wget -c https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-apt-config_0.8.13-1_all.deb sudo dpkg -i mysql-apt-config_0.8.13-1_all.deb
Après l’installation du paquet .deb, le programme de configuration se lance . Vérifiez que la configuration indique bien la version 8 et sélectionner la dernière ligne [Ok]
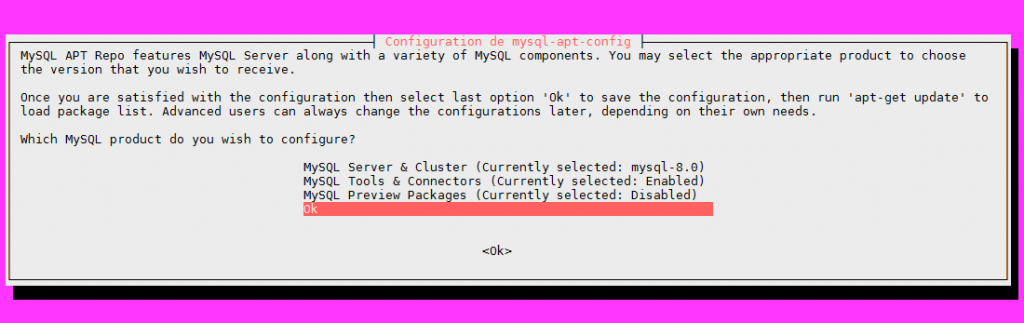
Ensuite, il convient de mettre à jour les paquets de votre serveur.
sudo apt-get update
Lancez ensuite l’installation du programme serveur de mysql
sudo apt install mysql-server
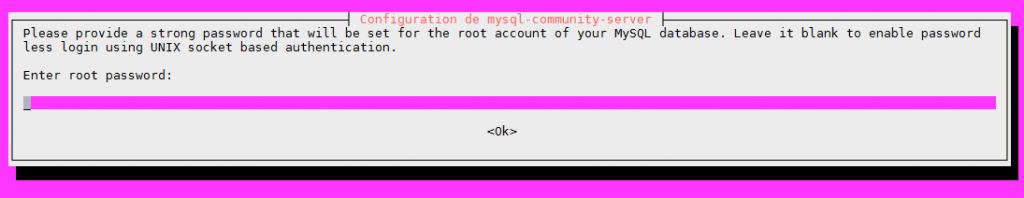
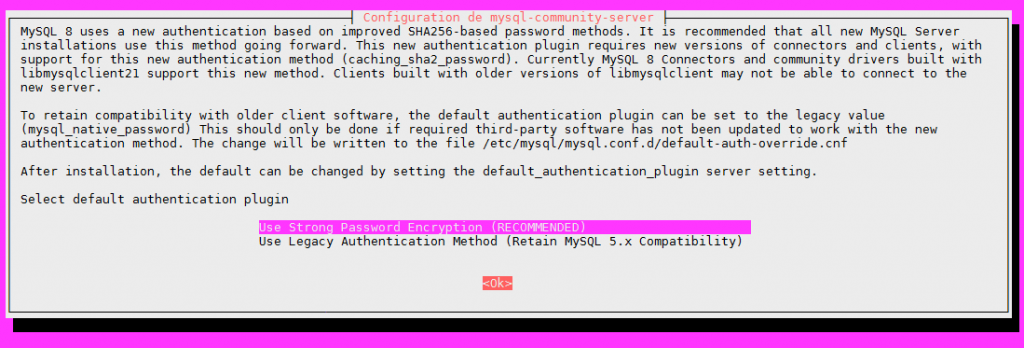
Par défaut l’installation n’est pas sécurisée. Il faut exécuter un script qui est installé avec le serveur MySQL et qui va permettre de définir notamment le compte root et de configurer l’accès en répondant à un certain nombre de questions
sudo mysql_secure_installation
La première question concerne l’activation du plugin pour gérer les mots de passe, qu’il faut activer (valeur : y)
VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN can be used to test passwords and improve security. It checks the strength of password and allows the users to set only those passwords which are secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD plugin? Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: y
Mettre un niveau medium (valeur : 1 )
There are three levels of password validation policy: LOW Length >= 8 MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 1
Entrez ensuite le mot de passe pour root et confirmez le
Please set the password for root here. New password:
Supprimez les accès anonymes sur la base (valeur : y)
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Supprimez les accès réseau de root (valeur : y)
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Supprimez la base de test (valeur : y)
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) :
Rechargez les droits (valeur : y) pour valider l’ensemble des choix
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) :
Il faut ensuite changer le mode d’accès de root pour passer de ‘auth_socket’ à ‘mysql_native_password’. Connectez-vous à mysql
sudo mysql
Vérifiez le mode de connexion de root
mysql> SELECT user,authentication_string,plugin,host FROM mysql.user;
+------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+ | user | authentication_string | plugin | host | +------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+ | root | | auth_socket | localhost | | mysql.session | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost | | mysql.sys | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost | | debian-sys-maint | *2F899ABF3C30971834C9A6C2EFCEFFAB851A64E1 | mysql_native_password | localhost | +------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
On voit que root est en mode ‘auth_socket’. Pour changer ce mode tapez la commande sql suivante en précisant le mot de passe dans le champ 'monmotdepasse'
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'monmotdepasse';
Validez les modifications apportées
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Vérifiez que le compte root se connecte avec le plugin ‘mysql_native_password‘
mysql> SELECT user,authentication_string,plugin,host FROM mysql.user; +------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+ | user | authentication_string | plugin | host | +------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+ | root | *17DD10419701818E6AA8C5989C8587FF7C8A8C43 | mysql_native_password | localhost | | mysql.session | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost | | mysql.sys | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost | | debian-sys-maint | *2F899ABF3C30971834C9A6C2EFCEFFAB851A64E1 | mysql_native_password | localhost | +------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Quittez Mysql
exit
Installation de Apache
Lancez l’installation
sudo apt install apache2
Activer le module userdir et le module rewrite
cd /etc/apache2/mods-available sudo a2enmod userdir sudo a2enmod rewrite sudo systemctl restart apache2
Installation PHP
lancer
sudo apt install libapache2-mod-php7.1 php7.1-mysql
Activer
sudo vi /etc/apache2/mods-available/dir.conf
DirectoryIndex index.html index.cgi index.pl index.php index.xhtml index.htm
Mettre
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html index.cgi index.pl index.xhtml index.htm
Activez PHP pour le mode userdir (par défaut, le moteur php n’est pas actif sur les comptes utilisateurs, il faut mettre en commentaire dans le fichier php7.2.conf, le engine Off )
cd /etc/apache2/mods-available sudo vi php7.2.conf
le fichier
<FilesMatch ".+\.ph(ar|p|tml)$">
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php
<FilesMatch ".+\.phps$">
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php-source
# Deny access to raw php sources by default
# To re-enable it's recommended to enable access to the files
# only in specific virtual host or directory
Require all denied
# Deny access to files without filename (e.g. '.php')
<FilesMatch "^\.ph(ar|p|ps|tml)$">
Require all denied
# Running PHP scripts in user directories is disabled by default
#
# To re-enable PHP in user directories comment the following lines
# (from to .) Do NOT set it to On as it
# prevents .htaccess files from disabling it.
#
#
# php_admin_flag engine Off
#
#
Pour connaitre la configuration utiliser pour php (apache2 ou cli)
php --ini
Modifiez ensuite la configuration
$ cd /etc/php/7.1/cli/ ou cd /etc/php/7.1/apache2/ $ sudo vi php.ini
; Defines the default timezone used by the date functions ; http://php.net/date.timezone date.timezone = europe/paris ; Maximum allowed size for uploaded files. ; http://php.net/upload-max-filesize upload_max_filesize = 200M
restart
sudo systemctl restart apache2